What's FAD TOOLS?
Fad Tools is a collection of three foundation design modules used to design and analyze foundations for transmission line structures.
- MFAD
- HFAD
- TFAD
Each module is based on a semi-empirical models developed from full-scale foundation tests and calibrated for Reliability Based Design (RBD).
MFAD (Moment Foundation Analysis and Design)
- MFAD designs and analyzes drilled shaft and direct embedded pole foundations subject to high overturning loads (moment and horizontal shear) and axial loads. Overturning loads are resisted by a combination of lateral pressure, vertical shear forces, base shear and moment.
- MFAD uses a Load Resistance Foundation Design (LRFD) method and models multi‐layered soil and rock subsurface conditions.
- MFAD uses a four spring model to resist the applied loading.
- MFAD springs can be turned on/off to model various soil–structure interaction conditions.
- MFAD results include nominal and design capacities.
- MFAD includes performance criteria for total rotation and deflection and non‐recoverable rotation and deflection.
- MFAD is calibrated with full‐scale load test of both direct embedded pole and drilled shaft foundations.
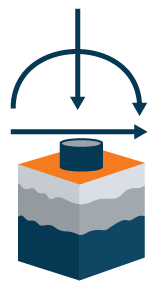
Drilled Shaft Model:
- Four‐spring load‐deflection model
- Up to 9 design load cases
- Models soil‐structure interaction in soil and rock subsurface profiles
- Option for steel and reinforcement design for drilled shaft foundations
Direct Embedment Model:
- Two‐spring load‐deflection model
- Up to 9 design load cases
- Models soil‐structure interaction in soil and rock subsurface profiles
- Option for concrete or soil backfill material
HFAD (H-frame Foundation Analysis and Design)
- HFAD designs and analyze drilled shaft and direct embedded foundations for H‐frame steel pole structures.
- HFAD models a foundation subjected to a combination of overturning loads (moment and horizontal shear) and uplift compression or shear loads.
- HFAD uses a Load Resistance Foundation Design (LRFD) method and models multi‐layered soil and rock subsurface conditions.
- HFAD results include nominal and design capacity.
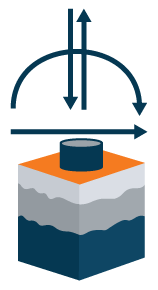
Drilled Shaft Model:
- Lateral spring resists moment and shear loads
- Cylindrical shear resists uplift loads
- Cylindrical shear and bearing capacity resist compression loads
- Models soil‐structure interaction in soil and rock subsurface profiles
- Option for steel and reinforcement design for drilled shaft foundations
Direct Embedment Model:
- Lateral spring resists moment and shear loads
- Cylindrical shear resists uplift loads
- Cylindrical shear resists compression loads
- Models soil‐structure interaction in soil and rock subsurface profiles
- Option for concrete or soil backfill material
TFAD (Tower Foundation Analysis and Design)
- TFAD designs drilled shaft foundations for lattice tower structure legs.
- TFAD models a foundation subjected to a combination of horizontal shear under uplift or compression loads.
- TFAD uses a Load Resistance Foundation Design (LRFD) method and models multi‐layered soil and rock subsurface conditions.
- TFAD results include nominal and design capacity.
- The TFAD cylindrical shear model is calibrated with full-scale Uplift load tests.
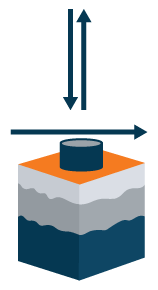
Drilled Shaft Model:
- Lateral spring resists normal and shear loads
- Cylindrical shear resists uplift loads
- Cylindrical shear and bearing capacity resist compression loads
- Models soil‐structure interaction in both soil and rock subsurface conditions
- Option for steel and reinforcement design
